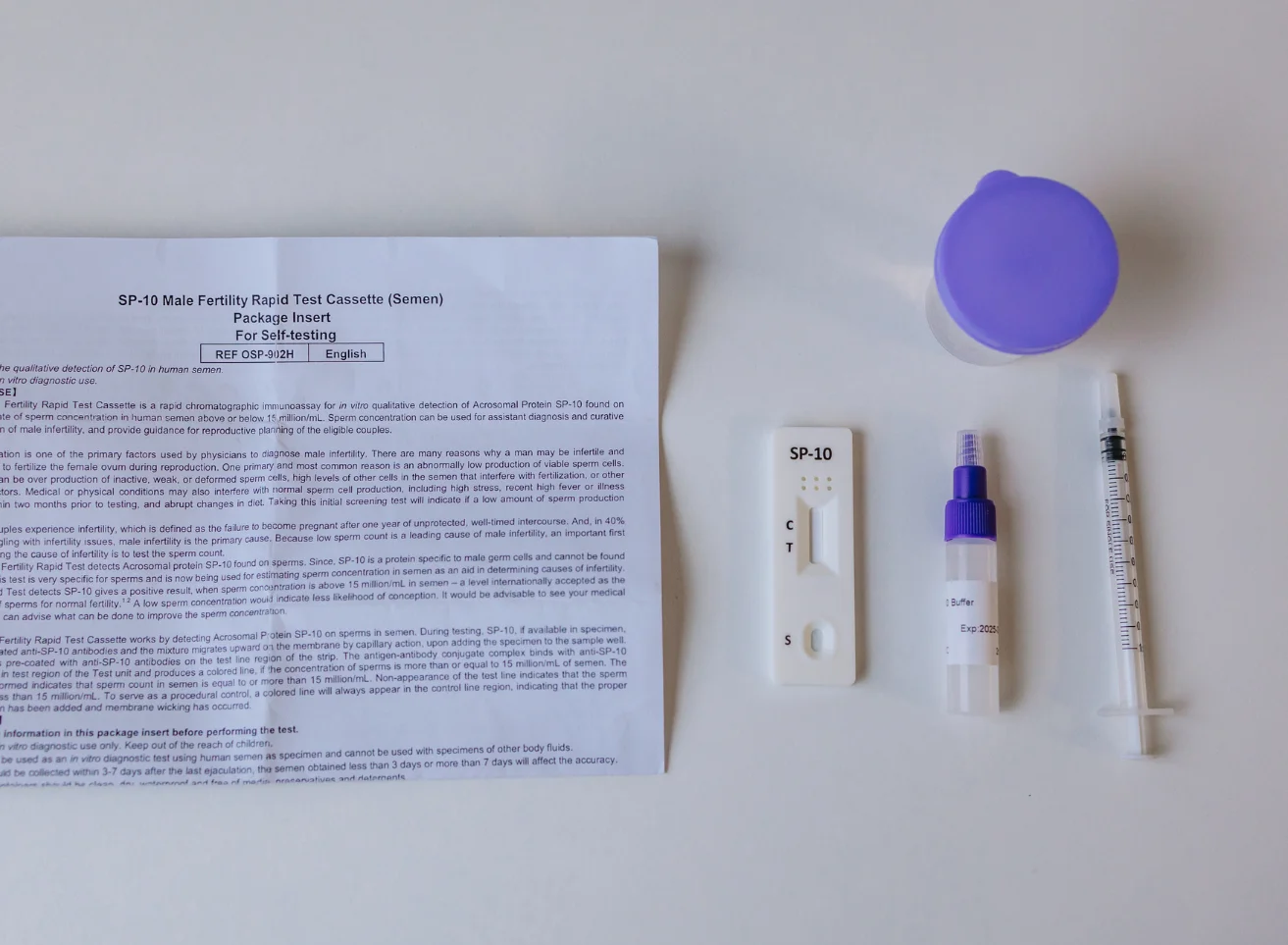
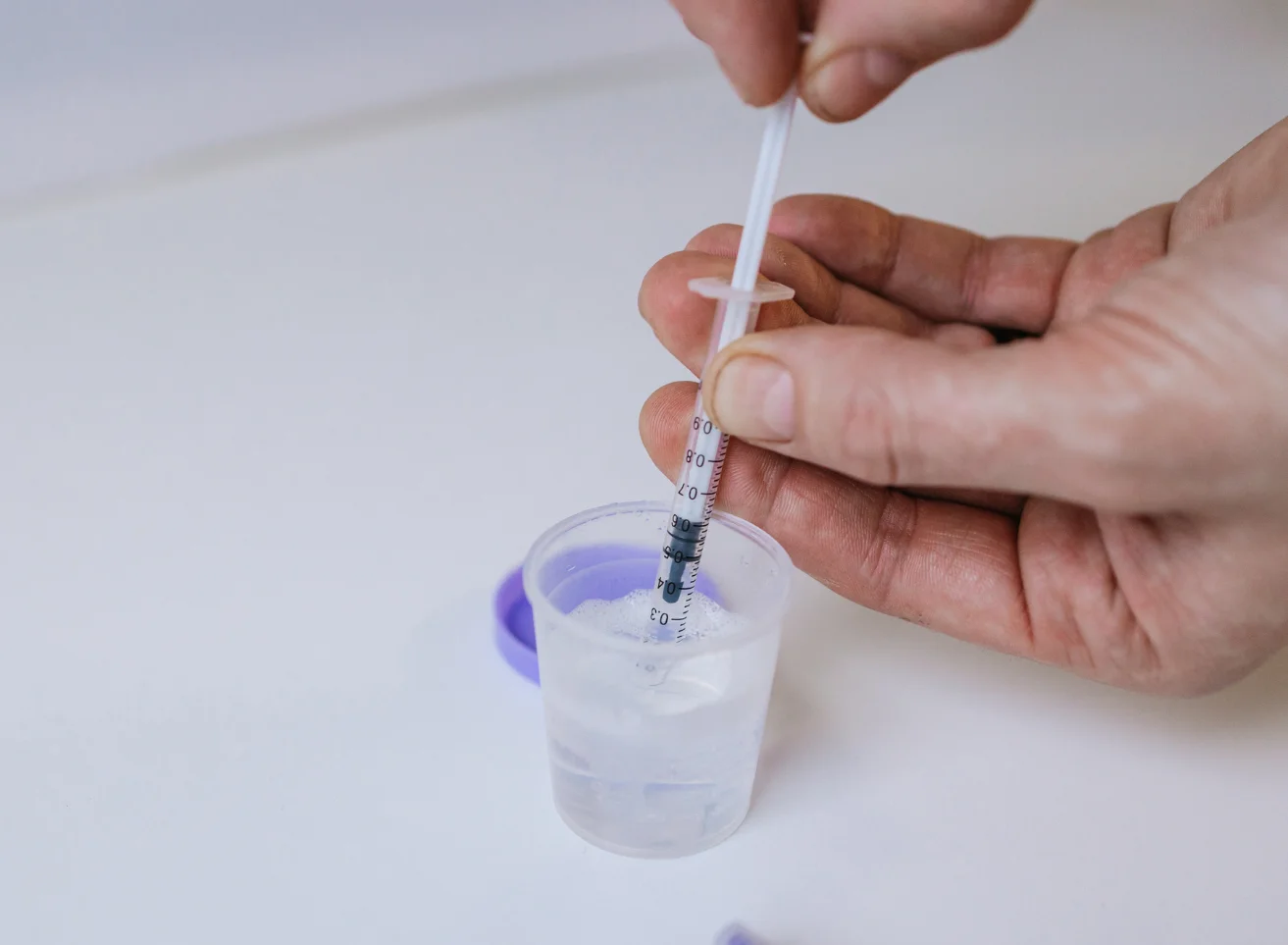
Infertility is usually defined as the inability of a couple to conceive after one year or more of unprotected, frequent sexual intercourse. There are many different causes of infertility, both male and female. Approximately 20% of infertility cases are as a result of male infertility; male infertility also plays a contributing factor in another 30-40% of all infertility cases[2] .
In the male reproductive system, infertility is often caused by the absence or low levels of sperm, abnormal shape or movement of the sperm, or problems with the ejection of sperm. A low sperm count is classified as the presence of fewer than 15 million sperm per 1mL of semen. Having a low sperm count can make it more difficult to conceive naturally.
There are many causes of low sperm count, some reversible and some irreversible.
Low sperm count may be associated with, but not limited to, the following:
- A hormone imbalance, such as reduced hormone production (hypogonadism)
- A genetic problem such as Klinefelter syndrome
- Previous surgery on the testicles or hernia repairs
- A structural problem – for example the tubes that carry the sperm being damaged or blocked by illness of injury.
Issues with sperm count may exist alongside issues with sperm morphology or motility, and female fertility issues, the results of the Male Fertility Test do not constitute a medical diagnosis and should be used as a guide to seek further medical advice with respect to fertility as a whole.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4691969/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562258/
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/infertility
- https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/infertility/index.htm